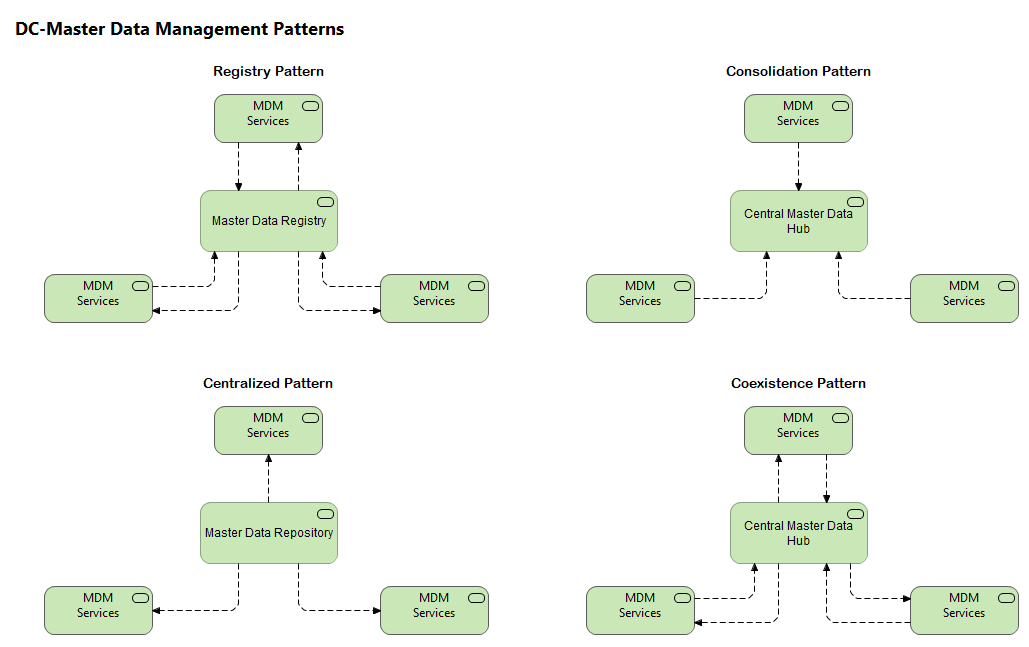
The Registry Pattern is mainly used to spot duplicates by running cleansing and matching algorithms on data from your various source systems. It assigns unique global identifiers to matched records to help identify a single version of the truth.
With a Consolidation pattern, the master data is generally consolidated from multiple sources in a central MD hub to create a single version of truth, otherwise known as the golden record.
A golden record is stored in the central MD hub and used for reporting and reference. However, any updates made to the master data are then applied to the original sources.
The Coexistence pattern allows you to construct a golden record in the same way as the Consolidation style, but your master data is stored in the central MD Hub and updated in its ource systems. Master data changes can happen in the Central MD Hub, as well as in the application systems. All attributes of the master data model must be consistent and cleansed before uploading them into the Master Data Management system.
The Centralized pattern allows storage and maintenance of master data attributes using linking, cleansing, matching and enriching algorithms to enhance the data. The enhanced data can then be published back to its respective source system. With this architecture, the master data hub supports the merging of master records, and source systems can subscribe to updates published by the central system to give complete consistency. The Centralized style also allows you to create master data making your MDM the system of record.